Iran's Drone Power: Unpacking A Global Military Shift
The landscape of modern warfare is constantly evolving, and at the forefront of this transformation is the rise of unmanned aerial vehicles (UAVs), commonly known as drones. Among the nations making significant strides in this domain, Iran stands out as a prominent player. The development and proliferation of Iranian UAVs have reshaped regional security dynamics and drawn considerable international attention, making them a critical subject for understanding contemporary geopolitical tensions.
Iran's journey into drone technology began decades ago, driven by strategic imperatives and a need to overcome conventional military disadvantages. What started as a nascent program has blossomed into a sophisticated and diverse fleet of unmanned systems, impacting conflicts far beyond its borders. This article delves into the origins, capabilities, strategic significance, and global implications of Iran's growing drone arsenal, offering a comprehensive look at how these aerial assets have become a cornerstone of the nation's military doctrine.
Table of Contents
- The Genesis of Iran's UAV Program
- Strategic Imperatives and Doctrine
- Key Iranian Drone Models and Capabilities
- Operational Deployment and Regional Impact
- Global Proliferation and Controversies
- Countermeasures and Vulnerabilities
- The Future of Iran's Drone Ambitions
- Conclusion
The Genesis of Iran's UAV Program
Iran's interest in unmanned aerial vehicles is not a recent phenomenon. Facing a conventional air force largely composed of aging equipment from the 1970s, a legacy compounded by decades of international sanctions, the nation sought asymmetric advantages. It was then that Iran started investing heavily in drones. This strategic pivot was a pragmatic response to its military vulnerabilities, aiming to compensate for the limitations of its traditional air power. The Iranian government has since been open about its interest in UAVs, viewing them not just as military tools but also as a means to enhance the prestige of Iran as a state capable of fielding modern military capabilities in the eyes of domestic and international audiences.
- Valerie Cruz
- Who Is Sanaa Lathan Married To
- Porn Actress Vanessa Del Rio
- Terri Welles Playmate
- Erica Herman Age
The journey began with modest efforts in the 1980s during the Iran-Iraq War, focusing primarily on basic reconnaissance. However, it was in the early 2000s that Iran started manufacturing UAVs on a more significant scale, laying the groundwork for its indigenous production capabilities. This commitment to self-sufficiency was crucial, as sanctions severely limited access to foreign military hardware. The Islamic Revolutionary Guard Corps Aerospace Force is the primary operator of Iran’s growing fleet of UAVs, although most Iranian military services employ them, showcasing the widespread integration of drones across its armed forces. This foundational period established Iran as a serious contender in the global drone landscape, driven by necessity and a long-term vision for defense.
Strategic Imperatives and Doctrine
The development of Iranian UAVs is deeply intertwined with Iran's broader military doctrine, which emphasizes asymmetric warfare, deterrence, and power projection in the region. Armed UAVs are viewed in Iran as a way to compensate for the vulnerabilities of its conventional air force, which dates to the 1970s and struggles to keep up with the times given the sanctions still imposed on the country. This strategic gap has made drones an indispensable asset, offering a cost-effective alternative to traditional manned aircraft for a variety of missions.
Drones serve as a multifaceted asset within Iran’s military strategy, enabling the Iranian armed forces to conduct critical operations in various domains. These unmanned aerial vehicles (UAVs) play significant roles in intelligence gathering and targeted strikes, reshaping how Iran engages in conflict. Their ability to operate in contested airspace, gather real-time intelligence, and deliver precision strikes with minimal risk to human life makes them ideal for Iran's regional objectives. Furthermore, Iranian drones are considered relatively inexpensive compared to their Western counterparts, providing a significant cost-benefit advantage that allows Iran to field a large and increasingly sophisticated fleet without crippling its defense budget. This economic efficiency further bolsters their strategic appeal, allowing for widespread deployment and proliferation among Iran's allies and proxies, thereby extending its influence.
- Christine Whigham
- Mario Casas Sierra
- Dacre Montgomery Girlfriend
- Nickelback Chad Kroeger Wife
- Janet Hunt
Key Iranian Drone Models and Capabilities
Iran has developed a range of drones, each with its unique characteristics and capabilities, reflecting a concerted effort to build a comprehensive and versatile unmanned fleet. From reconnaissance to combat, these drones represent the cutting edge of Iran's indigenous defense industry. The launch of the Ababil UAV marked Iran’s entry into indigenous UAV production, a significant milestone that paved the way for more advanced systems. The successful deployment of the Shahed series further enhanced both reconnaissance and combat capabilities, becoming a cornerstone of Iran's drone arsenal.
Beyond these foundational models, Iran has continued to innovate. Iran unveiled advanced drones like the Karrar and Mohajer series, emphasizing combat readiness and precision strikes. These developments highlight Iran's ambition to not only produce drones but to continuously improve their performance, range, and lethality. While the Iranian government did not provide a demonstration of the UAV flying, or state what its range was for some models, public displays and operational reports offer insights into their growing sophistication. The display marks the first time these models have been displayed in the same place, underscoring Iran's confidence in its drone technology.
Reconnaissance and Intelligence Gathering
A primary function of many Iranian UAVs is intelligence, surveillance, and reconnaissance (ISR). Drones like the Mohajer series have been extensively used for monitoring borders, tracking adversary movements, and gathering critical battlefield intelligence. Their ability to loiter over targets for extended periods provides valuable real-time data, which is crucial for strategic planning and tactical execution. This persistent surveillance capability allows Iran to maintain a watchful eye over its interests and potential threats in the region.
For instance, there have been instances where Iranian drones were suspected of conducting surveillance operations in neighboring countries. Officials at Iraq's defence and interior ministries suggested that a drone might have been scouting for routes to smuggle Iranian weapons into the country. The New York Times, however, speculated that the drone was monitoring Iranian dissidents in Iraq, such as those at Camp Ashraf, which is located near where the drone crashed. These varied interpretations underscore the dual-use nature and strategic ambiguity often associated with Iranian UAV operations, making their true intent difficult to ascertain definitively.
Combat and Strike Capabilities
Beyond intelligence gathering, Iran has significantly invested in armed drones capable of precision strikes. The Hamaseh drone, an unmanned aerial vehicle of Iranian origin adopted in 2013, represents an early step into this capability. However, it is the more advanced Shahed-136 and Karrar models that have truly transformed Iran's offensive drone capabilities. These loitering munitions, often referred to as "kamikaze drones," are designed to hit targets with high accuracy, making them potent tools for asymmetric warfare.
The successful deployment of the Shahed series, enhancing both reconnaissance and combat capabilities, has been particularly noteworthy. These drones have demonstrated the capacity for long-range strikes, posing a significant threat to adversaries. While it remains unclear how they’ve been used in combat in all instances, their reported use in various regional conflicts and the recent attack on Israel in April of last year, where Iran launched missiles and drones after a strike on Iran's consulate in Damascus was widely attributed to Israel, highlight their operational readiness. Although the Israeli military intercepted the vast majority of these projectiles, the incident underscored the growing threat posed by Iran's armed UAVs.
Operational Deployment and Regional Impact
Iranian UAVs have become a pervasive element in the Middle East's complex security landscape. Their deployment extends beyond Iran's borders, often through proxies and allied groups, amplifying Iran's influence and projecting its power without direct military engagement. This strategy allows Iran to engage in conflicts at arm's length, supporting its regional objectives while minimizing direct accountability.
How Iran’s drones threaten Israel is a particularly acute concern for regional stability. Learn more about the Iranian drones sent in an attempt to attack Israel as retaliation for Operation Rising Lion. This incident, among others, demonstrates the direct threat perception. Beyond Israel, Iranian drones have been observed or used in conflicts across Iraq, Syria, Yemen, and potentially other flashpoints. According to senior military officials and independent analysis by the Global Terrorism Trends and Analysis Center (GTTAC), which provides data to the State Department’s Counterterrorism Bureau, most attack unmanned aerial vehicles (UAVs) used in the world today originate from Iran. This widespread proliferation, often under US watch, underscores the significant impact of Iranian drone technology on regional and global security.
The strategic utility of these drones lies in their ability to conduct targeted strikes, disrupt enemy operations, and gather critical intelligence in contested areas. This has allowed Iran and its allies to challenge air superiority traditionally held by adversaries and to conduct operations that would otherwise be too risky or costly for conventional forces. The increasing sophistication and reach of these drones mean that their operational deployment will likely continue to expand, further complicating efforts to de-escalate tensions in the Middle East.
Global Proliferation and Controversies
The proliferation of Iranian UAVs extends beyond the Middle East, drawing significant international controversy. The most prominent example involves allegations of Iran supplying drones to Russia for use in the conflict in Ukraine. While Iran foreign ministry continued to deny sending weapons for use in the war, accusations from Western nations persist.
This controversy highlights the dual challenge posed by Iran's drone program: its direct use by Iran and its proliferation to other state and non-state actors. The international community, particularly the United States and European Union, has imposed sanctions on Iran related to its drone program, aiming to curb its development and export. However, despite these measures, the global footprint of Iranian drones appears to be growing, raising concerns about their impact on international stability and the rules of engagement in modern warfare. The dispute over evidence of Russian use of Iranian drones underscores the difficulty in verifying and attributing the source of such weapons, further complicating diplomatic efforts.
Countermeasures and Vulnerabilities
As Iran's drone capabilities grow, so too do efforts by its adversaries to develop countermeasures and exploit potential vulnerabilities. The interception of Iranian drones and missiles by the Israeli military in April 2024 demonstrates the effectiveness of advanced air defense systems against such threats. This incident highlighted the ongoing technological arms race between offensive drone capabilities and defensive counter-drone systems.
Beyond direct interception, intelligence operations play a crucial role. Among the targets reportedly prosecuted by Israeli operatives within Iran was an air defense site near Tehran, suggesting efforts to disrupt the very infrastructure supporting Iran's drone operations. Furthermore, there have been reports of sophisticated counter-operations, such as Israel smuggling attack drones into Iran using a variety of means, including trucks, shipping containers, and even suitcases, the Wall Street Journal reported on Sunday, citing sources familiar. These covert operations aim to degrade Iran's capabilities, gather intelligence, or even conduct targeted strikes within Iran itself, demonstrating the multi-layered approach to countering the drone threat.
Despite their advantages, Iranian UAVs are not invulnerable. Their reliance on GPS for navigation, susceptibility to electronic warfare, and potential for exploitation through cyber means represent weaknesses that adversaries can exploit. The effectiveness of countermeasures will continue to evolve as both sides adapt to the changing nature of drone warfare, making this a critical area of ongoing development and intelligence gathering.
The Future of Iran's Drone Ambitions
Iran's drone program shows no signs of slowing down. The strategic importance of Iranian UAVs to the nation's defense and foreign policy ensures continued investment and innovation. Iran separately said it had provided two types of ballistic missiles to its army and the guard on Tuesday, including one named for Soleimani, indicating a broader push for advanced military capabilities that likely includes further integration of drones with missile technology.
The future trajectory of Iran's drone ambitions will likely involve several key areas:
- Increased Autonomy: Developing drones with greater autonomous capabilities, reducing reliance on human operators and increasing their effectiveness in complex environments.
- Swarm Technology: Researching and developing drone swarm capabilities, where multiple UAVs operate collaboratively to overwhelm enemy defenses.
- Integration with Other Systems: Further integrating drones with naval, ground, and missile forces to create a more cohesive and formidable military network.
- Export and Proliferation: Despite sanctions, Iran may continue to export its drone technology to allies and proxies, further expanding its global footprint and challenging international non-proliferation efforts.
- Counter-Stealth and Advanced Sensors: Investing in technologies that allow drones to detect and engage stealth aircraft or operate more effectively in contested airspace.
The ongoing displays of new models and the public claims of increased capabilities suggest that Iran views its drone program as a cornerstone of its future military strength. This continued evolution will undoubtedly have profound implications for regional stability and global security dynamics, making the monitoring and understanding of Iranian UAV developments a crucial task for defense analysts and policymakers worldwide.
Conclusion
The rise of Iranian UAVs represents a significant shift in modern military capabilities, driven by Iran's strategic needs and its indigenous technological advancements. From their humble beginnings to their current status as a diverse and formidable fleet, these drones have become an indispensable component of Iran's defense strategy, enabling intelligence gathering, precision strikes, and power projection across the Middle East and beyond. Their cost-effectiveness and versatility have allowed Iran to circumvent conventional military disadvantages imposed by sanctions, reshaping regional conflicts and challenging established military doctrines.
However, the proliferation of Iranian drones also brings complex challenges, fueling regional tensions and drawing international condemnation. As adversaries develop sophisticated countermeasures, the technological arms race in drone warfare will undoubtedly intensify. Understanding the nuances of Iran's drone program, its strategic rationale, and its global impact is essential for anyone seeking to comprehend the evolving landscape of 21st-century warfare. The story of Iranian UAVs is far from over; it is a dynamic narrative of innovation, strategic adaptation, and geopolitical consequence that will continue to unfold. We encourage you to share your thoughts on this critical topic in the comments below or explore other articles on our site for more in-depth analyses of global security issues.
- Who Is Ashley Judd Married To
- Sloane Momsen
- Nicki Minaj Relationship
- Elizabeth Anne Millsap
- Nickelback Chad Kroeger Wife
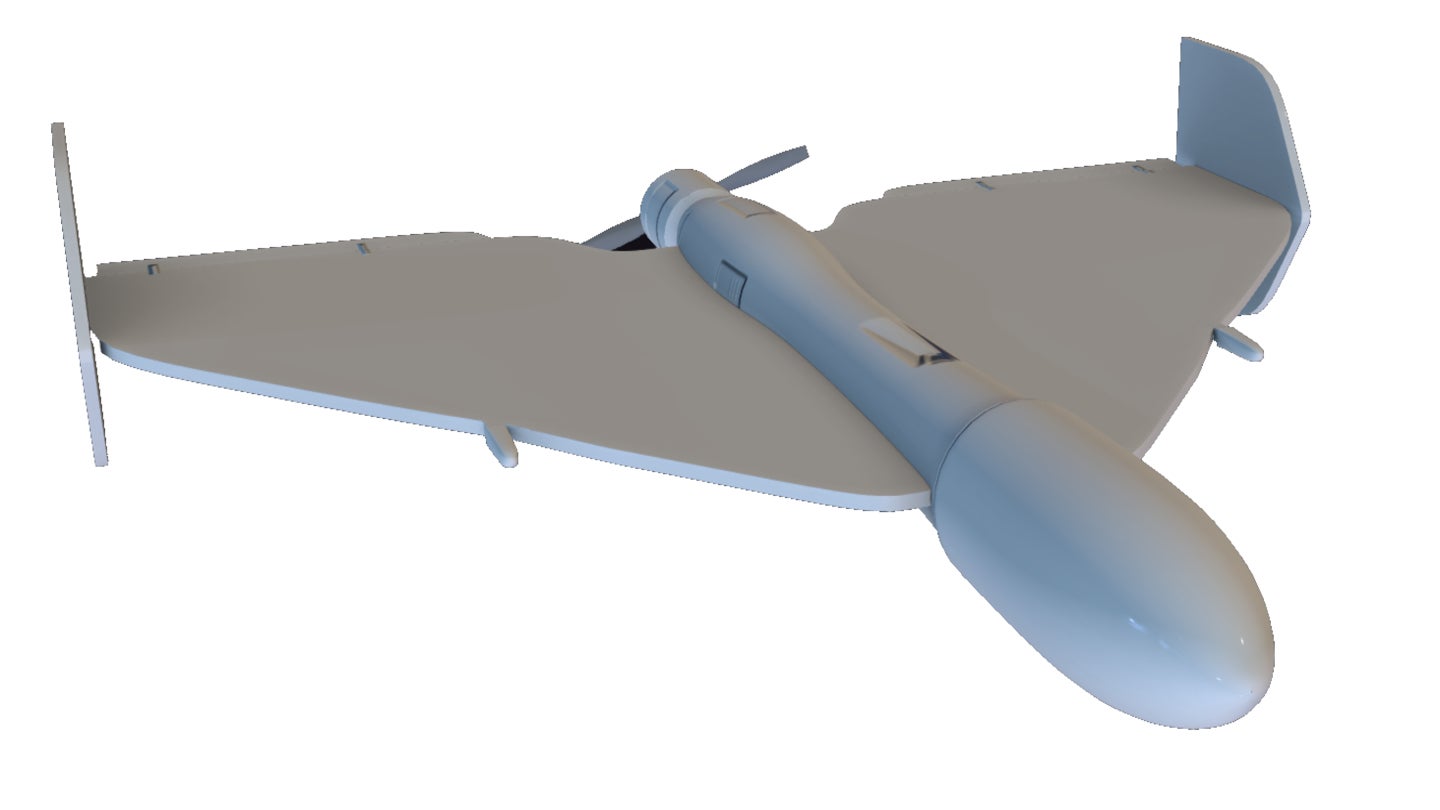
Shahed-136 Kamikaze UAV, Iran

Israeli Media: 6 Drones Bombed UAV Base in Iran

Drone Revolution In Iran! After 'Longest-Range' UAV, IRGC To Launch