Unveiling Iran: Where Ancient Persia Meets Modern Geopolitics
When the question "donde esta Iran" or "where is Iran" arises, it's more than just a simple geographical query; it's an invitation to explore a nation steeped in millennia of history, rich cultural heritage, and profound geopolitical significance. Often a focal point in international discussions, understanding Iran's precise location and its surrounding context is fundamental to grasping its past, present, and future role on the global stage.
This article aims to provide a comprehensive answer to "where is Iran," delving into its exact geographical coordinates, its diverse landscapes, its storied history, and its contemporary relevance. By exploring these facets, we hope to offer a clearer picture of this influential country in Western Asia, moving beyond headlines to illuminate the deep roots of its identity and importance.
Table of Contents
- Pinpointing Iran: A Geographical Overview
- The Diverse Tapestry of Iranian Landscapes
- A Journey Through Time: Iran's Rich History
- Iran's Political and Administrative Structure
- The Strategic Importance of Iran's Location
- Culture, Economy, and Global Relations
- Understanding Iran's Global Impact
- Addressing "Donde Esta Iran" in the Modern Context
Pinpointing Iran: A Geographical Overview
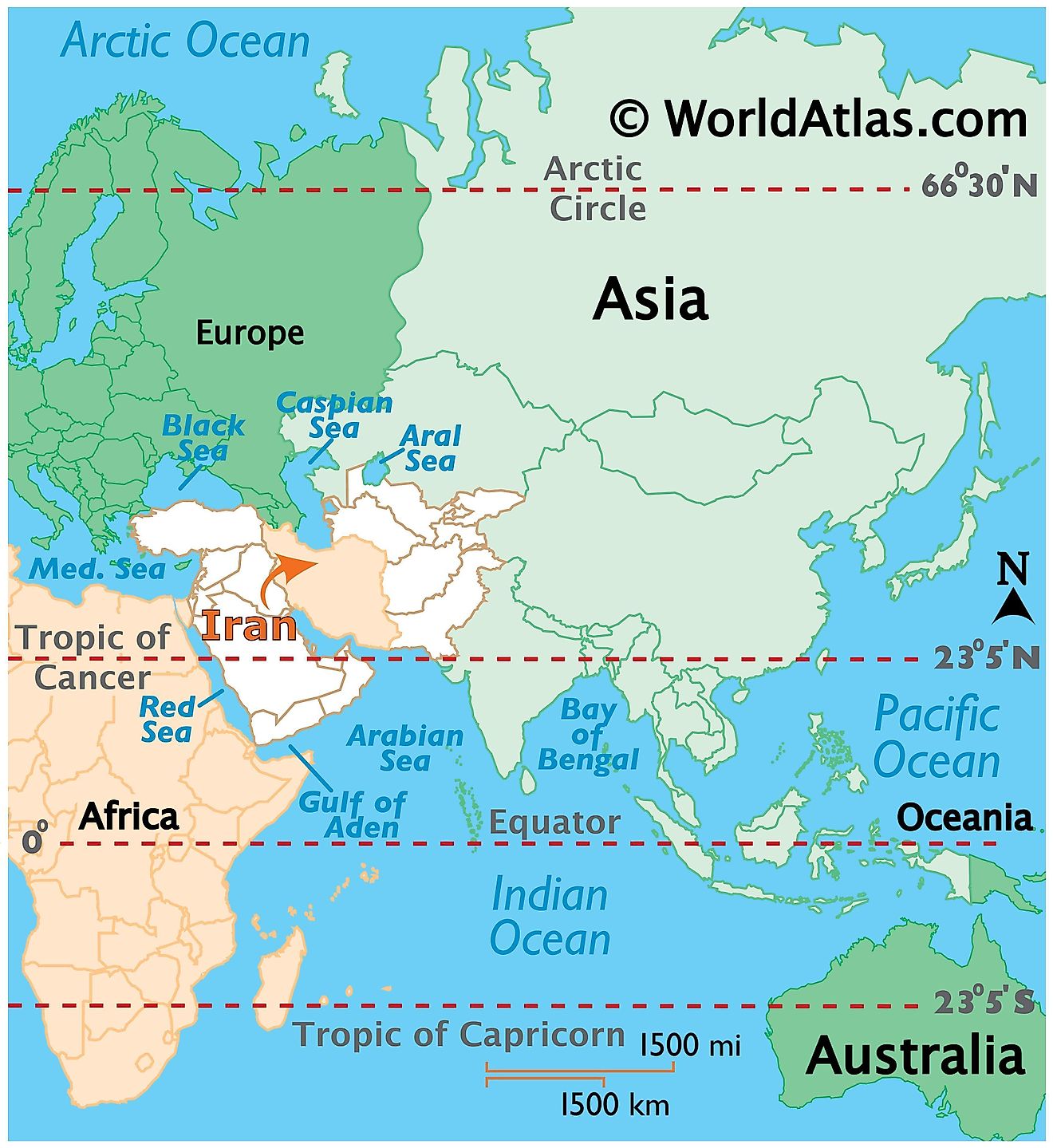
To truly understand Iran, the first step is to precisely answer the question: where is Iran located on the world map? Iran, officially known as the Islamic Republic of Iran, is a country situated in the southwestern part of the Asian continent, specifically within the region commonly referred to as the Middle East or West Asia. It holds a unique position, straddling a critical juncture of continents and cultures.
- Logan Paul Dating History
- Nickelback Chad Kroeger Wife
- Faye Maltese
- Sam Sorbo Age
- Jamal Murray Girlfriend
The Heart of Western Asia
Iran lies in both the northern and eastern hemispheres of the Earth. Its conventional placement as the easternmost country of the Middle East underscores its role as a bridge between the Arab world, Central Asia, and the Indian subcontinent. This strategic positioning has historically made it a crossroads for trade, empires, and cultural exchange, shaping its identity profoundly. When you look at a map, you'll see Iran nestled between major landmasses and significant bodies of water, defining its unique geographical character.
Borders and Maritime Connections
Iran shares extensive land and sea borders, which are crucial to its geopolitical standing. To the north, Iran borders the Caspian Sea, the world's largest inland body of water, and shares land boundaries with Turkmenistan, Azerbaijan, and Armenia. This northern frontier connects Iran to Central Asia and the Caucasus region, facilitating cultural and economic ties.
To the west, Iran shares long borders with Iraq and Turkey, two nations with whom it has complex historical and contemporary relationships. These western borders are vital for regional trade and security dynamics.
Moving eastward, Iran is bordered by Afghanistan and Pakistan. These eastern frontiers are often characterized by rugged terrain and significant challenges related to security and cross-border movements.
Finally, to the south, Iran's extensive coastline stretches along the Persian Gulf and the Gulf of Oman. These vital waterways provide Iran with direct access to international shipping lanes and are central to global energy trade. The Persian Gulf, in particular, is a critical artery for oil and gas exports, making Iran a key player in the global energy market. Its location between the Caspian Sea in the north and the Persian Gulf and the Gulf of Oman in the south is a defining geographical feature, offering both opportunities and strategic vulnerabilities.
Size and Scale: How Big is Iran?
Iran is not just strategically located; it is also a vast country in terms of land area. With a total area of approximately 1,648,195 square kilometers (1,648,000 km² is also commonly cited), Iran ranks among the largest countries in Asia and is the 18th largest in the world. To put this into perspective, this area is roughly 3.3 times the size of Spain, highlighting its immense geographical diversity.
Its extensive landmass is complemented by a substantial coastline, totaling approximately 2,440 kilometers, primarily along its southern maritime borders. This vast territory supports a significant population, estimated to be over 80 million inhabitants, making it one of the most populous nations in the Middle East. The sheer scale of Iran means that its geography is incredibly varied, encompassing everything from towering mountains to vast deserts and fertile coastal plains, each contributing to its unique character.
The Diverse Tapestry of Iranian Landscapes
Beyond simply answering "where is Iran," it's essential to appreciate the dramatic and varied landscapes that define its territory. Iran is widely recognized as one of the most mountainous countries in the world, with its topography playing a crucial role in shaping its climate, population distribution, and cultural development.
Mountain Ranges and Plateaus
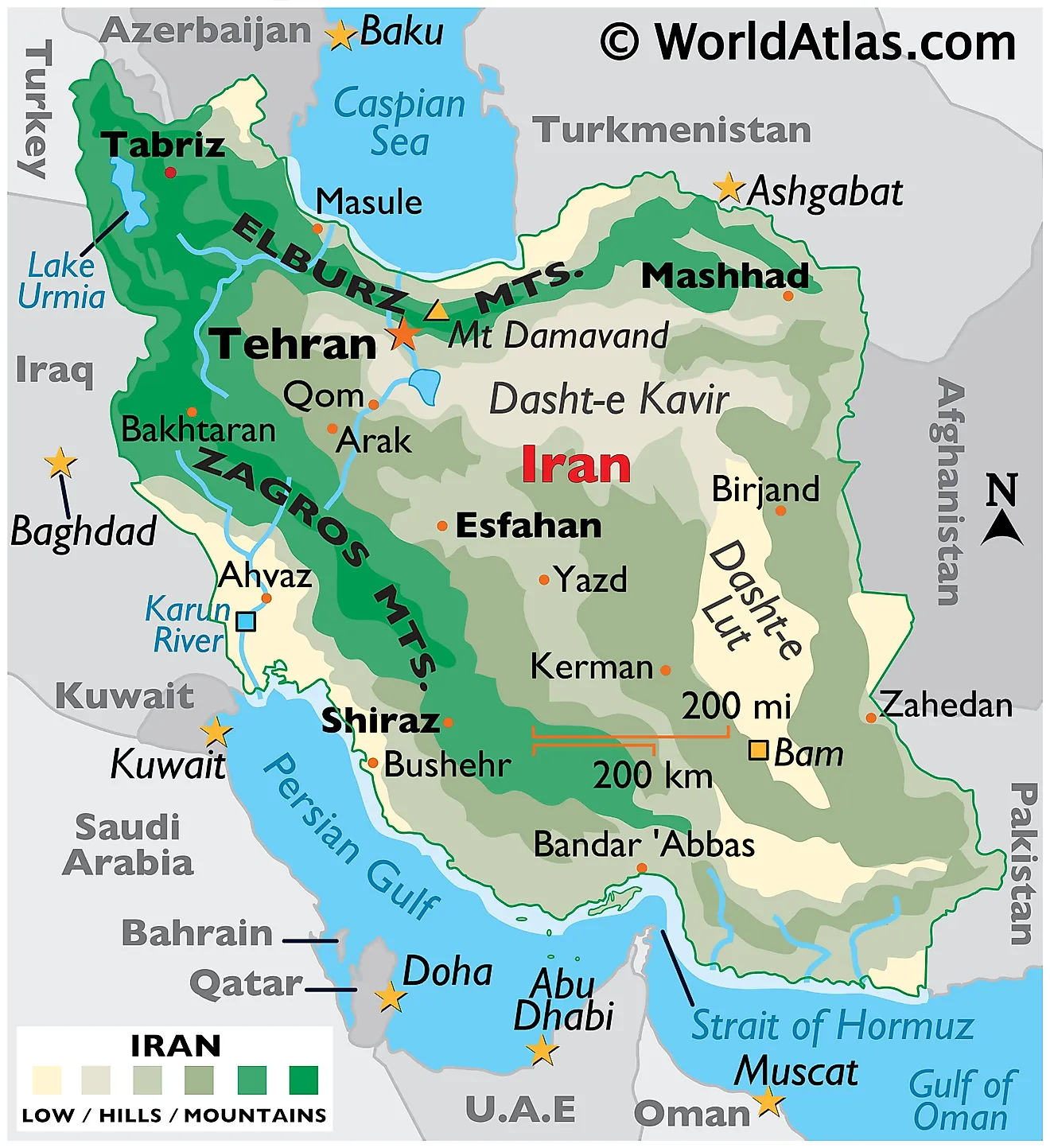
Iran is largely situated within the Alpidic mountain belt, a vast system of mountain ranges that extends across Eurasia. The most prominent of these are the Zagros Mountains, which stretch from the northwest to the southeast, forming a natural barrier that has historically influenced human settlement and movement. These rugged mountains are characterized by deep valleys and high peaks, providing both challenges and resources for the local population.
To the north, the Elburz Mountains run parallel to the Caspian Sea, creating a formidable natural barrier. Within the Elburz range stands Mount Damavand, a majestic volcanic peak rising to 5,671 meters. Damavand is not only the highest point in Iran but also the highest mountain in Eurasia west of the Hindu Kush, making it a significant geographical landmark. The Iranian plateau, a central feature of the country's geography, is formed by a Precambrian shield, considered an extension of the Arabian shield. This elevated plateau, surrounded by mountain ranges, defines much of Iran's interior, contributing to its arid and semi-arid conditions.
Climates Across the Nation
Given its vast size and varied topography, Iran exhibits a wide range of climatic conditions. The majority of Iran is arid or semi-arid, characterized by low rainfall and significant temperature fluctuations between day and night. However, there are notable exceptions.
Along the Caspian Sea coast, a subtropical climate prevails, marked by lush vegetation, higher humidity, and more moderate temperatures. This fertile strip is sustained by the moisture trapped by the Elburz Mountains, which act as a natural barrier. The Sefid River is one of the few waterways that cuts through this barrier, providing vital irrigation.
In the northwest, winters are cold with intense snowfall, and temperatures often drop below freezing in December and January. Spring and autumn are relatively mild, offering pleasant conditions. In contrast, the summers across most of the country, especially on the central plateau, are typically dry and hot, with temperatures soaring. This diverse climate mosaic influences everything from agricultural practices to the daily lives of Iranians, demonstrating how deeply the answer to "where is Iran" is tied to its environmental realities.
A Journey Through Time: Iran's Rich History
Understanding "where is Iran" geographically is incomplete without acknowledging its profound historical depth. The land known today as Iran has been a cradle of civilization for millennia, serving as the heartland of some of the world's most influential empires and cultures. It was formerly known as Persia to the Western world, a name that still evokes images of ancient grandeur and sophisticated empires.
From Ancient Persia to the Islamic Republic
The ancient peoples of Iran, including the Medes, who emerged during the 2nd millennium BCE, as well as the Persians and Parthians, laid the foundations for a powerful civilization. The Medes unified to form the Median Empire around 728 BCE, a precursor to one of history's most expansive and enduring empires. In 550 BCE, under the visionary leadership of Cyrus the Great, the Achaemenid Empire was established. This empire stretched from the Balkans to the Indus Valley, introducing innovations in governance, infrastructure, and human rights that left an indelible mark on subsequent civilizations.
Following the Achaemenids, Iran experienced various periods of rule, including the Seleucid, Parthian, and Sasanian empires, each contributing to its rich cultural tapestry. The arrival of Islam in the 7th century CE marked a pivotal turning point, leading to the establishment of Islamic rule and the eventual formation of the Islamic Republic of Iran in 1979. This long and complex history, filled with periods of immense power, cultural flourishing, and foreign invasion, has shaped the Iranian identity, fostering a deep sense of pride in its heritage and a unique cultural resilience.
Iran's Political and Administrative Structure
The modern political landscape of Iran is defined by its status as the Islamic Republic of Iran, with Tehran serving as its bustling capital. The country's administrative organization, while rooted in ancient traditions, has undergone significant modernization in recent history.
The current territorial organization is relatively modern. In 1950, Iran was reorganized into 10 numbered provinces, each with governments subordinate to the central authority in Tehran. These governorates were subsequently elevated to provincial status between 1960 and 1981, reflecting a gradual decentralization of administration while maintaining central control. Today, Iran is divided into 31 provinces, each with its own capital and administrative apparatus, designed to manage local affairs while adhering to national policies. This structure helps govern a country with a vast area, estimated at around 1,745,150 square kilometers, ensuring that services and governance reach its diverse population across varied geographical regions. Understanding this administrative framework is key to comprehending how the nation functions, regardless of where is Iran on the map.
The Strategic Importance of Iran's Location
The answer to "where is Iran" extends far beyond mere coordinates; it defines the nation's profound strategic importance in global affairs. Its geographical position at the nexus of the Middle East, Central Asia, and the Caucasus has historically made it a coveted territory and a vital conduit for trade, culture, and military power.
Geopolitical Crossroads
Iran's location between the resource-rich Caspian Sea to the north and the oil-laden Persian Gulf and Gulf of Oman to the south places it at the heart of global energy dynamics. A significant portion of the world's oil and gas reserves are located in or around the Persian Gulf, making Iran a crucial player in the energy market. Its control over the Strait of Hormuz, a narrow waterway at the mouth of the Persian Gulf, through which a substantial percentage of the world's seaborne oil passes, gives it immense leverage in international relations.
This strategic choke point, coupled with its extensive land borders with key regional actors like Iraq, Turkey, Afghanistan, and Pakistan, makes Iran a central figure in regional security and stability. Its geopolitical significance is often highlighted in international news, with global attention frequently focused on its foreign policy, nuclear program, and regional influence. The question of "where is Iran" thus quickly transforms into a discussion about its role in complex geopolitical narratives, including its historical tensions and diplomatic engagements with various international powers and neighboring states.
Culture, Economy, and Global Relations
Iran possesses an incredibly rich history and a vibrant cultural heritage that spans millennia. This heritage is evident in its ancient ruins, magnificent architecture, exquisite Persian carpets, and profound literary traditions. Persian poetry, in particular, is celebrated worldwide, with figures like Rumi, Hafez, and Saadi leaving an enduring legacy. The country's cultural depth offers a stark contrast to the often-simplistic portrayal it receives in international media.
Economically, Iran is a major player in the global energy market, largely due to its vast reserves of oil and natural gas. These resources form the backbone of its economy, though the country has also invested in diversifying its industrial base, including petrochemicals, automotive manufacturing, and mining. Despite facing various international sanctions, Iran maintains significant trade relationships and seeks to expand its economic partnerships globally.
Iran's global relations are complex and multifaceted. As an influential country in the Middle East, it plays a significant role in regional dynamics, engaging with both allies and adversaries. Its foreign policy is shaped by a blend of historical grievances, national interests, and ideological principles. For anyone seeking detailed and updated information about Iran to better understand this influential country, exploring its geography, history, culture, economy, and international relations provides a holistic perspective. The answer to "where is Iran" is therefore not just about a dot on the map, but about a complex nation deeply intertwined with global events.
Understanding Iran's Global Impact
The geographical reality of "where is Iran" directly underpins its considerable global impact. Its location as a bridge between East and West, its vast energy resources, and its rich historical and cultural legacy collectively contribute to its unique standing. Iran's influence is felt in various spheres, from regional security architectures to global energy markets and cultural exchanges.
Its strategic position allows it to exert significant influence over key maritime routes and land corridors, making it a critical actor in any discussion concerning the stability of the Middle East and Central Asia. Furthermore, its substantial population and a vibrant intellectual tradition mean that Iran is a source of both innovation and cultural richness. Understanding Iran's place in the world requires appreciating this intricate web of geographical, historical, economic, and cultural factors that define its global footprint. It is a country that consistently draws international attention, and its trajectory significantly impacts regional and global dynamics.
Addressing "Donde Esta Iran" in the Modern Context
In contemporary discourse, the question "donde esta Iran" often arises in the context of geopolitical tensions and international relations. Whether it's discussions about regional conflicts, energy security, or diplomatic initiatives, Iran's geographical and political positioning is always central. For instance, recent international focus on regional conflicts and the ongoing dynamics in the Middle East often highlight Iran's role, prompting many to ask about its location and significance. The country's time zone, GMT+3:30, further emphasizes its unique position on the global clock, reflecting its distinct geographical and cultural alignment.
The exploration of "where is Iran" is therefore a journey into understanding a country that is simultaneously ancient and modern, geographically diverse, and geopolitically pivotal. It is a nation that has shaped history and continues to shape the present, demanding a nuanced understanding that goes beyond simplistic labels. By appreciating its geographical context, its historical journey from ancient Persia to the Islamic Republic, and its complex web of international relations, we gain a more complete picture of this fascinating and important nation.
Conclusion
In conclusion, the question "donde esta Iran" unveils a country of immense geographical, historical, and geopolitical significance. Iran is strategically located in Western Asia, bordered by the Caspian Sea to the north, the Persian Gulf and Gulf of Oman to the south, and a host of countries including Turkmenistan, Azerbaijan, Armenia, Turkey, Iraq, Afghanistan, and Pakistan. Its vast and varied landscapes, from the towering Zagros and Elburz mountains to its arid plateaus and subtropical Caspian coast, define its unique character and influence its climate and population distribution.
From its origins as ancient Persia, home to the mighty Achaemenid Empire, to its modern identity as the Islamic Republic, Iran boasts a rich cultural heritage and a complex history that continues to shape its present. Its strategic location, particularly concerning global energy routes, positions it as a key player in international affairs. Understanding Iran's geography, history, and political structure is essential for anyone seeking to comprehend the intricate dynamics of the Middle East and global geopolitics.
We hope this comprehensive overview has provided a clearer answer to "where is Iran" and illuminated the multifaceted nature of this influential nation. We encourage you to delve deeper into the rich tapestry of Iran's culture, history, and current affairs. Share your thoughts in the comments below, or explore other articles on our site to continue your journey of discovery into the complexities of our world.
- Mar%C3%ADa Fern%C3%A1ndez Ache
- Kim Christiansen Age 9news
- Marcia Gay Harden Partner
- Bret Bollinger Wife
- Who Is Whitney Cummings Dating
Mapas de Irán - Atlas del Mundo
Mapas de Irán - Atlas del Mundo
Iran - Smoke Tree Manor