Navigating Iran's Free Market Exchange Rate: A Comprehensive Guide
Understanding the intricate dynamics of the exchange rate in Iran's free market is crucial for anyone engaging with the country's economy, whether for business, travel, or personal remittances. Unlike many nations with a single, unified currency valuation, Iran operates under a complex dual-rate system, where the informal, open market rate often dictates the real economic landscape, starkly differing from the officially fixed rate. This unique environment presents both challenges and opportunities, requiring a nuanced understanding of its underlying mechanisms and influential factors.
This article delves deep into the complexities of the Iranian Rial (IRR) in the free market, exploring how it functions, what drives its fluctuations, and how individuals can stay informed about its live movements. We will examine the interplay between the official and informal rates, demystify the Rial-Toman conversion, and highlight reliable sources for tracking real-time currency values. By the end, readers will gain a comprehensive perspective on navigating this distinctive financial terrain, empowering them to make more informed decisions.
Table of Contents
- Understanding Iran's Dual Exchange Rate System
- The Toman and Rial: Navigating Daily Transactions
- Key Factors Influencing Iran's Free Market Exchange Rate
- How to Access Free Market Exchange Rates
- Tracking Live Exchange Rates: Reliable Sources and Tools
- The Impact of Free Market Rates on Daily Life and Business
- Historical Trends and Future Outlook
- Navigating Currency Exchange Safely and Wisely
Understanding Iran's Dual Exchange Rate System
Iran's currency landscape is characterized by a unique dual exchange rate system, a significant factor for anyone looking into the exchange rate in Iran's free market. This system features an official rate, formally fixed by the Central Bank of Iran (CBI), and an informal, open market rate. The latter is the rate at which foreign currencies are actually bought and sold by the public through currency exchange shops and street traders, often referred to as the "street rate" or "black market rate." This divergence is not merely a technicality; it profoundly impacts economic activities and daily life within the country.
The Official Rate vs. The Free Market Rate
The official exchange rate, set by the Central Bank of Iran, is typically used for specific government transactions, essential imports, and state-backed enterprises. It aims to stabilize prices for basic goods and manage the flow of foreign currency for strategic purposes. However, this rate often remains artificially low compared to the true market value of the Iranian Rial. Consequently, access to foreign currency at the official rate is highly restricted and usually reserved for specific, pre-approved entities or purposes.
In contrast, the free market exchange rate reflects the actual supply and demand dynamics for foreign currencies like the USD, EUR, and GBP among the general public and businesses. This is where most individuals and private sector entities conduct their foreign exchange transactions. The free market rate is typically significantly higher than the official rate, making foreign currency more expensive for those who rely on the open market. The existence of these two rates creates arbitrage opportunities and a complex pricing structure for goods and services.
Why the Discrepancy Matters
The gap between the official and free market rates has far-reaching implications. For importers, access to the cheaper official rate means lower costs for raw materials or finished goods, potentially leading to lower prices for consumers (if those savings are passed on). However, if they are forced to source foreign currency from the free market, their costs skyrocket, contributing to inflation and higher consumer prices. For ordinary citizens, the free market rate directly impacts the purchasing power of their savings, especially if they hold foreign currency, and the cost of imported goods, travel, and remittances.
This dual system also introduces significant uncertainty and risk into the Iranian economy. Businesses face challenges in planning and budgeting due to volatile exchange rates. The constant fluctuation of the exchange rate in Iran's free market can erode profits for companies dealing with international trade and make long-term investments more precarious. Furthermore, it can foster a parallel economy where foreign currency is hoarded as a hedge against inflation and currency depreciation, further exacerbating the supply-demand imbalance in the open market.
The Toman and Rial: Navigating Daily Transactions
Beyond the dual exchange rates, another layer of complexity in Iran's currency system is the interplay between the Rial and the Toman. While the Iranian Rial (IRR) is the official currency, used for all banknotes, coins, and formal financial transactions, the Toman is the unit of account predominantly used in daily payments and informal commerce. This can be a source of confusion for foreigners and even for locals accustomed to the informal system.
The conversion is straightforward: one Toman is equal to ten Rials. Essentially, when people refer to prices in Tomans, they are simply dropping one zero from the Rial value. For example, if something costs 50,000 Rials, people will commonly say it costs 5,000 Tomans. This practice has become so ingrained in Iranian daily life that it's rare to hear prices quoted in Rials in casual conversation or market transactions. When checking live Iranian Rial (IRR) exchange rates, it's vital to remember that while the official currency is Rial, daily payments and purchasing in Iran mostly use Tomans as the main circulation money. This means that if a currency converter shows a USD value in Rials, you'll need to mentally (or physically) drop a zero to understand its Toman equivalent for practical purposes.
For instance, if the live price of the US Dollar in the open market is quoted as 938,000 Rials (as it was on Thursday, June 19, 2025, according to some reports), most Iranians would intuitively understand this as 93,800 Tomans. This mental conversion is second nature for locals but can trip up visitors or those new to the Iranian economic context. Therefore, when tracking the exchange rate in Iran's free market, always be mindful of whether the quoted rate is in Rials or Tomans, especially when dealing with smaller denominations or daily purchases. Experience seamless currency conversions by keeping Toman as your base currency for mental calculations, even if the raw data is in Rial.
Key Factors Influencing Iran's Free Market Exchange Rate
The exchange rate in Iran's free market is highly sensitive to a confluence of internal and external factors. Unlike more stable economies where interest rates and trade balances are primary drivers, Iran's currency market is often swayed by geopolitical developments, economic sanctions, and domestic policy decisions. Understanding these influences is key to anticipating currency movements and making informed financial decisions.
Economic Sanctions and Geopolitical Tensions
Perhaps the most dominant factor affecting the Iranian Rial's value in the free market is the pervasive economic sanctions imposed by international powers, particularly the United States. These sanctions severely restrict Iran's ability to export oil, access international banking systems, and attract foreign investment. This leads to a chronic shortage of foreign currency within the country, driving up the demand for available dollars, euros, and other major currencies in the free market. Any news related to sanctions – their imposition, lifting, or tightening – can cause immediate and significant shifts in the free market rate.
Geopolitical tensions in the region and internationally also play a critical role. Escalations in conflicts, diplomatic disputes, or even political rhetoric can trigger panic buying of foreign currency as individuals and businesses seek to protect their assets from potential economic instability. Conversely, signs of de-escalation or diplomatic breakthroughs can lead to a temporary strengthening of the Rial. The perception of risk, whether real or perceived, directly impacts the confidence in the local currency and, by extension, the exchange rate in Iran's free market.
Inflation and Domestic Economic Policies
High domestic inflation is another relentless pressure on the Iranian Rial. When the cost of living rises rapidly, the purchasing power of the Rial diminishes. People naturally seek to convert their savings into more stable assets, primarily foreign currencies or gold, to preserve their wealth. This increased demand for foreign exchange further devalues the Rial in the free market. The Central Bank's monetary policies, including interest rates and money supply, also influence inflation and, consequently, the exchange rate. For instance, if the government prints more money to cover budget deficits, it can fuel inflation and weaken the Rial.
Government policies related to foreign trade, import restrictions, and foreign exchange regulations also have a direct impact. Attempts to control the free market or restrict access to foreign currency can sometimes backfire, leading to even greater volatility and a widening gap between the official and free market rates. The overall health of the Iranian economy, including oil revenues (despite sanctions), non-oil exports, and domestic production, also contributes to the supply of foreign currency and thus influences the exchange rate in Iran's free market. For example, a recent observation noted that the US Dollar faced a price increase in the open market, reaching 938,000 Rials on June 19, 2025, an increase of 33,000 Rials (3.65%) from the previous day, which had already seen an increase of 1000 Rials. Such daily fluctuations underscore the sensitivity of the market to underlying economic pressures and expectations.
How to Access Free Market Exchange Rates
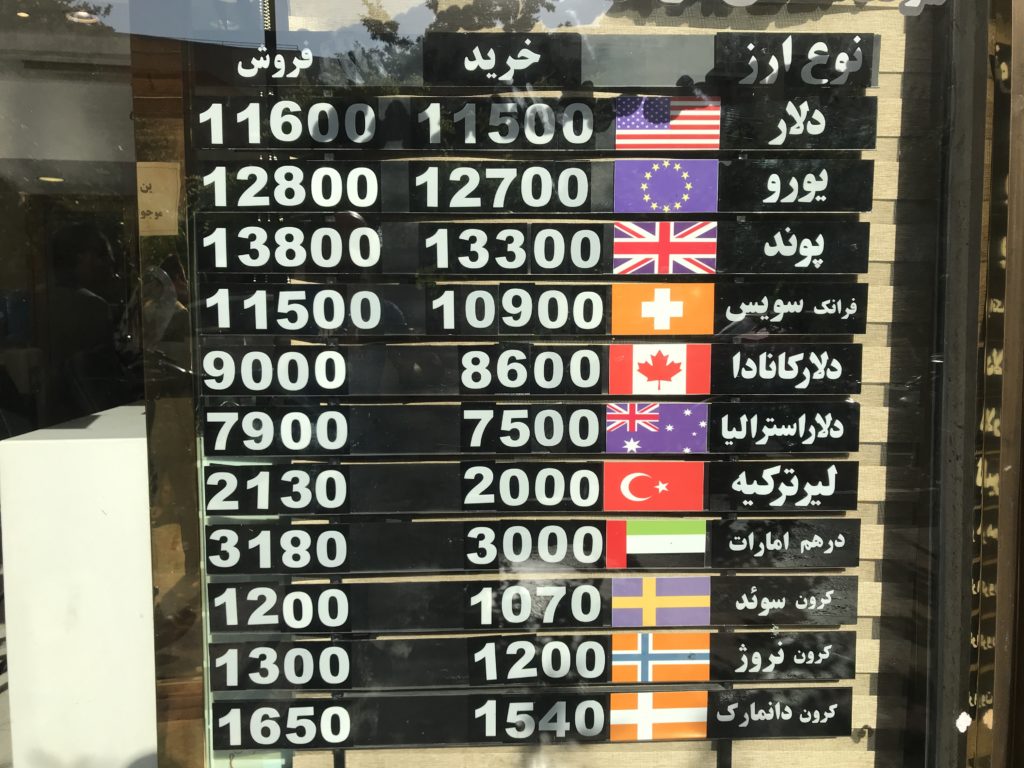
For anyone needing to exchange currency or simply track the value of the Iranian Rial, accessing reliable free market exchange rates is paramount. Unlike official bank rates, the free market rates are dynamic and can vary slightly between different exchange points. The primary avenues for obtaining these rates are currency exchange shops and online platforms.
**Currency Exchange Shops:** Throughout major Iranian cities, particularly in bustling areas, you'll find numerous licensed currency exchange shops (known as "Sarrafi"). These establishments openly display their buy and sell rates for various currencies, including USD, EUR, GBP, CAD, and more. They are a common point for locals and visitors to exchange foreign currency for Rials (or Tomans). While generally reliable, it's always wise to compare rates from a few different shops to ensure you're getting the best deal, as slight variations can occur. These shops are the physical manifestation of the open market, reflecting the immediate supply and demand for foreign currency.
**Online Platforms and Apps:** In the digital age, several online platforms and mobile applications provide live updates on the exchange rate in Iran's free market. These platforms aggregate data from various sources, including the physical market, to provide a comprehensive and up-to-the-minute view. They are particularly useful for those outside Iran or for anyone who needs to quickly check rates without visiting a physical shop. These digital tools often offer currency converters, charts showing historical trends, and even gold prices in the free market. They serve as a quick and accurate reference for checking currency prices, providing live exchange rates for dollar and euro in Iran's free market.
It's important to note that while street traders might also offer exchange services, using licensed exchange shops is generally safer and more reliable. They operate under regulations and provide receipts, offering a layer of security that street transactions might lack. The goal is always to get the most accurate and current spot exchange rate of Iranian Rial (IRR) against major currencies like the US Dollar index, Canadian Dollar, and others.
Tracking Live Exchange Rates: Reliable Sources and Tools
Staying updated with the latest buy and sell rates for various currencies is essential when dealing with the Iranian market. Given the volatility of the exchange rate in Iran's free market, real-time data is invaluable. Several platforms have emerged as go-to sources for accurate and reputable foreign exchange trading data.
**Bonbast:** This platform is widely recognized as one of the most accurate and reputable foreign exchange trading data collectors for the Iranian market. Bonbast provides live exchange rates for today, including the US Dollar, Euro, Turkish Lira, Iranian Rial, and other currencies in Iran's free market. Its reliability makes it a primary reference for individuals and businesses alike. Users can get Iranian Rial rates, charts, and use an IRR currency converter directly on the site. Bonbast's strength lies in its ability to quickly reflect changes in the open market, offering a clear picture of the current price of the US dollar, the remittance price of the US dollar, along with a dollar price chart.
**Other Online Converters and Financial News Sites:** Many financial news websites and general currency converter tools also provide data for the Iranian Rial. While useful for quick checks, it's crucial to verify their data against more specialized Iranian market trackers like Bonbast, especially for critical transactions. Look for features such as:
- Live exchange rates for 170+ world currencies and gold coins.
- Iranian Rial (IRR) currency converter, often allowing conversion with Toman as your base currency.
- Ability to convert cryptocurrencies like Bitcoin to Iranian Rial and any world currency.
- Currency charts (e.g., USD to IRR currency chart) showing historical data and dynamics of cost as a percentage for the day.
These tools help users access Iranian Rial in black market exchange rates for 28+ currencies, providing comprehensive information for both buying and selling prices. Staying informed through these reliable sources is the best way to navigate the often-unpredictable fluctuations of the exchange rate in Iran's free market.
The Impact of Free Market Rates on Daily Life and Business
The pervasive influence of the exchange rate in Iran's free market extends far beyond financial transactions, deeply embedding itself into the fabric of daily life and significantly shaping the operational landscape for businesses. Its volatility and the wide gap from the official rate create a unique economic environment that demands constant adaptation.
**For Individuals:**
- **Purchasing Power:** The free market rate directly impacts the purchasing power of ordinary Iranians. As the Rial depreciates against major currencies like the USD and EUR, imported goods – from electronics and medicines to certain food items – become more expensive. This contributes to inflation and erodes the value of savings held in Rials.
- **Travel and Remittances:** For those traveling abroad or receiving money from relatives overseas, the free market rate is the de facto conversion rate. A weaker Rial means that foreign currency goes further when converted into local currency for expenses within Iran, but it also means that Iranians need significantly more Rials to purchase foreign currency for travel or to send remittances abroad.
- **Investment and Savings:** Many Iranians view foreign currencies, particularly the US dollar, and gold as a hedge against inflation and the depreciation of the Rial. This drives demand in the free market, sometimes leading to speculative bubbles and rapid price increases, as observed when the US dollar increased by 3.65% in a single day, reaching 938,000 Rials on June 19, 2025.
**For Businesses:**
- **Import/Export Costs:** Businesses involved in international trade are heavily impacted. Importers who cannot access the official rate must purchase foreign currency at the higher free market rate, increasing their operational costs and ultimately the prices of their products. Exporters, conversely, benefit from a weaker Rial as their goods become cheaper in foreign currency terms, potentially boosting competitiveness, but they also face challenges in repatriating foreign earnings.
- **Pricing and Profit Margins:** Companies often struggle to set stable prices for their products and services due to fluctuating input costs tied to the free market exchange rate. This uncertainty can squeeze profit margins and make long-term financial planning extremely difficult.
- **Investment Decisions:** The unpredictable nature of the free market rate deters foreign direct investment and makes domestic investment riskier. Businesses may postpone expansion plans or large capital expenditures due to the high currency risk.
In essence, the free market rate acts as a barometer of economic confidence and stability within Iran. Its movements directly translate into real economic consequences, influencing everything from the price of bread to the viability of a large-scale industrial project.
Historical Trends and Future Outlook
The history of the Iranian Rial, particularly its performance in the free market, is a chronicle of significant volatility, largely shaped by geopolitical events and domestic economic policies. Understanding these historical trends provides valuable context for assessing the future outlook of the exchange rate in Iran's free market.
**Historical Depreciation:** Over the past few decades, the Iranian Rial has experienced substantial depreciation against major global currencies. This trend accelerated significantly following the re-imposition of international sanctions, particularly after 2018. Periods of heightened political tension, such as the withdrawal from the JCPOA (Joint Comprehensive Plan of Action) or regional conflicts, have consistently led to sharp declines in the Rial's value. For example, historical data, often found in "Iran currency exchange rate history" charts, clearly illustrates these dramatic shifts. The Canadian Dollar in relation to the Iranian Rial on charts shows the dynamics of cost as a percentage over time, highlighting periods of rapid depreciation. The USD to IRR currency chart similarly provides a free live currency conversion chart for US Dollar to Iran Rial, showcasing its long-term weakening trend.
During these periods, the demand for foreign currency as a safe haven asset surges, driving the free market rate to unprecedented levels. The government's attempts to control the market, such as setting official rates or restricting access to foreign currency, have often proven ineffective in the face of overwhelming market forces, further widening the gap between the official and free market rates.
**Future Outlook:** Predicting the future of the exchange rate in Iran's free market is inherently challenging due to the multitude of unpredictable variables. However, several key factors will likely continue to shape its trajectory:
- **Sanctions Relief:** Any significant progress towards the lifting or easing of international sanctions would likely be the most impactful factor in strengthening the Rial. This would increase
- Erica Herman Age
- Arnold Germer Age
- Gloria Carter Spann
- Yancy Butler Relationships
- Ambar Driscoll Age

The truth about the Iran currency exchange rate - VincePerfetto.com
The truth about the Iran currency exchange rate - VincePerfetto.com

Money exchange in Iran - Aseman Gasht