Unveiling Iran's Borders: A Comprehensive Map Guide
Iran, officially known as the Islamic Republic of Iran, is a nation of immense historical depth, rich cultural heritage, and profound geopolitical significance. Spanning a vast area in Western Asia, its geographical footprint and, crucially, its intricate border system, play a pivotal role in shaping regional dynamics. Understanding the Iran border map is not merely an exercise in geography; it's a deep dive into the strategic arteries of a country that stands at the crossroads of continents, influencing trade, security, and international relations. This article aims to provide a comprehensive exploration of Iran's borders, drawing insights from its diverse topography, strategic infrastructure, and the complex interplay of its relationships with neighboring nations.
From the towering peaks of the Elburz and Zagros mountains to the vast expanse of the Caspian Sea and the strategic waters of the Persian Gulf, Iran's boundaries are as varied as its landscapes. These borders are not just lines on a map; they are living frontiers that witness the flow of goods, people, and, at times, geopolitical tensions. Through a detailed examination of the Iran border map, we can better appreciate the nation's unique position and the multifaceted challenges and opportunities it faces in an ever-evolving global landscape.
Table of Contents
- Iran's Geographical Footprint: A Land of Vastness
- Navigating Iran's Extensive Land Borders
- Southern Shores: The Persian Gulf and Gulf of Oman
- The Political Landscape on the Iran Border Map
- Strategic Significance: Iran's Borders in a Volatile Region
- Geopolitical Tensions: The Iran-Israel Dynamic and Border Implications
- Exploring Iran Through Diverse Map Collections
- The Future of Iran's Borders: Challenges and Developments
Iran's Geographical Footprint: A Land of Vastness
Occupying an impressive 1,648,195 square kilometers (636,372 square miles) in Western Asia, Iran is a country of substantial size and diverse geographical features. This vastness is immediately apparent when examining any map of Iran, revealing a topography that ranges from arid deserts to lush forests and towering mountain ranges. The physical map of Iran distinctly shows the prominent Elburz Mountains in the north and the extensive Zagros Mountains stretching along Iran's western borders. These mountainous regions are not just geographical markers; they significantly influence climate, population distribution, and strategic considerations across the nation.
- Arnold Germer Age
- Who Is Sanaa Lathan Married To
- Sam Sorbo Age
- Nicki Minaj Relationship
- Porn Actress Vanessa Del Rio
Within the Elburz mountain chain, Mount Damavand stands as a majestic sentinel, reaching an impressive 18,934 feet (5,771 meters). This iconic peak, often marked on maps by a yellow triangle, is a testament to Iran's rugged natural beauty. Furthermore, the highlands of Iran are surprisingly home to some of the world's most unexpected glaciers. Their presence in what is largely a dry environment is incredibly advantageous, serving as a vital supply of fresh water for communities that depend on glacial ice. This unique combination of vast landmass, significant mountain ranges, and critical water sources underscores the complex environmental tapestry that defines Iran's geographical footprint, all clearly delineated on a detailed Iran border map.
Navigating Iran's Extensive Land Borders
Iran boasts one of the longest land borders of any country in Western Asia, extending an impressive 3,662 miles in length. This extensive perimeter is shared with seven distinct nations, each presenting its own set of historical, cultural, and geopolitical considerations. The detailed Iran border map clearly illustrates these shared frontiers, highlighting the intricate relationships Iran maintains with its neighbors. These seven countries are Iraq, Turkmenistan, Afghanistan, Pakistan, Turkey, Armenia, and Azerbaijan. Each segment of this vast border has its own unique characteristics, influencing everything from trade routes to regional security dynamics.
Western Frontiers: Iraq and Turkey
To the west, Iran shares significant land borders with Iraq and Turkey. The Iran-Iraq border, often depicted on specific maps like "iran iraq border map.png," is a historically sensitive and strategically vital line. This frontier has been the site of numerous conflicts and remains a critical area for regional stability. The shared border with Turkey, another major regional power, facilitates trade and cultural exchange but also presents challenges related to security and cross-border movements. Both these western borders are characterized by mountainous terrain, particularly the Zagros range, which influences accessibility and the establishment of border controls.
Northern Neighbors: The Caspian Sea and Beyond
Iran's northern boundary is defined by a combination of land borders and a vast body of water: the Caspian Sea. To the north, Iran is bounded by Azerbaijan, Armenia, and Turkmenistan. The shared land borders with these nations are crucial for regional connectivity and energy transit. Beyond the land, the Caspian Sea forms a significant part of Iran's northern perimeter. The "Iran borders length in north of Iran and the Caspian Sea region" highlights the importance of this unique inland sea, which is a source of natural resources and a critical waterway. The distance of the diameter of the country from northwest to southeast is about 2761 km, a measurement that underscores the vastness of Iran's northern reaches and its proximity to the Caucasus and Central Asian regions.
Eastern Edges: Afghanistan and Pakistan
To the east, Iran shares its borders with Pakistan and Afghanistan. The Iran-Pakistan boundary, visible on maps like "iran pakistan boundary.png," is a long and often challenging frontier, particularly known for issues related to illegal trade and drug smuggling. Similarly, the border with Afghanistan is a critical pathway for cross-border movements and has significant implications for regional security, given Afghanistan's own complex internal dynamics. These eastern borders traverse diverse landscapes, from deserts to rugged terrains, making border management a continuous and complex endeavor for Iranian authorities. The "Iran east road distance" and "Iran country size and borders length in east of Iran" data underscore the logistical challenges of managing these extensive eastern frontiers.
Southern Shores: The Persian Gulf and Gulf of Oman
While the focus often remains on Iran's extensive land borders, its southern maritime boundaries are equally, if not more, strategically vital. To the south, Iran is bounded by the Persian Gulf and the Gulf of Oman. These waterways are among the most important shipping lanes in the world, particularly for oil transport. The Strait of Hormuz, a narrow choke point connecting the Persian Gulf to the Gulf of Oman, is a critical artery for global energy supplies, and Iran's control over its northern shore grants it significant strategic leverage. The presence of these major maritime borders profoundly influences Iran's geopolitical standing, its naval capabilities, and its economic interactions with the wider world. The security and stability of these southern waters are constant priorities for Iran, making them a crucial aspect of the overall Iran border map.
The Political Landscape on the Iran Border Map
A political map of Iran offers more than just international borders; it provides a comprehensive overview of the nation's internal administrative structure and key urban centers. This type of Iran border map typically shows the national capital, Tehran, as the central hub of political and economic activity. Beyond Tehran, province capitals are clearly marked, illustrating the decentralized governance structure of the Islamic Republic of Iran. Major cities such as Esfahan, Kermanshah, and Tabriz are also prominently displayed, highlighting their significance as population centers, industrial hubs, and cultural landmarks.
Furthermore, a detailed political map often includes key infrastructure, such as main roads and railroads, which are essential for internal connectivity and cross-border trade. Major airports are also indicated, underscoring Iran's air transport capabilities and international links. Beyond contemporary infrastructure, these maps sometimes feature the location of historical landmarks like Persepolis, the ancient ceremonial capital of the Achaemenid Empire (c. 550–330 BC). This inclusion serves as a powerful reminder of Iran's deep historical roots and its enduring legacy, adding layers of meaning to the geographical and political lines drawn on the Iran border map.
Strategic Significance: Iran's Borders in a Volatile Region
The strategic importance of Iran's borders cannot be overstated, particularly given its location in a region characterized by complex geopolitical dynamics. The vastness of Iran's land borders, coupled with its critical maritime access, positions it as a pivotal player in Western Asia. These borders are not merely lines of demarcation but active zones of interaction, trade, and, at times, conflict. The sheer length of its land borders, shared with seven diverse nations, means Iran must maintain robust border security measures to manage various challenges.
One significant aspect of border management highlighted in the data is the ongoing effort to deter illegal trade crossings and drug smuggling. Projects are being implemented that include "large earth and stone embankments and deep ditches to deter illegal trade crossings and drug smuggling to both sides." These physical barriers underscore the serious nature of these cross-border threats and Iran's commitment to securing its frontiers. The strategic implications extend beyond direct border control; the stability of neighboring countries directly impacts Iran's own security. Therefore, understanding the nuances of each segment of the Iran border map is crucial for analyzing regional security architectures and the broader geopolitical landscape of Western Asia.
Geopolitical Tensions: The Iran-Israel Dynamic and Border Implications
The geopolitical tensions surrounding Iran extend far beyond its immediate neighbors, with the dynamic between Iran and Israel being a particularly prominent and volatile aspect. While not sharing a direct border, the "map above compares Israel vs Iran on a number of dimensions," emphasizing the significant disparity in size and population: "Iran is much, much bigger than Israel (around 75x bigger). It also has lots more people." This size difference, however, does not diminish the intensity of their rivalry, which often plays out indirectly across the region and through targeted operations.
Maps detailing "Iran’s nuclear program" and "Israeli airstrikes in cities like Tehran, Esfahan, Kermanshah, and Tabriz" reveal a critical dimension of this tension. These maps highlight "Iran nuclear sites and Israeli strikes," providing a visual representation of the strategic targets involved. For instance, the data mentions a hypothetical "Operation Rising Lion" launched by Israel on June 13, 2025, "targeting Iran’s missile and nuclear program." This interactive map "highlights the locations of direct attacks on Iranian territory attributed to Israel, along with Iran’s key military and nuclear facilities." Conversely, "Iranian strikes on locations in Israel" and "numerous missile barrages" illustrate Iran's retaliatory capabilities. This complex interplay of strikes and counter-strikes, though not directly on a shared physical border, profoundly impacts the security considerations around Iran's frontiers, making the broader Iran border map a lens through which to view these regional power dynamics.
Exploring Iran Through Diverse Map Collections
The study of Iran's geography, infrastructure, and strategic importance is significantly enhanced by a diverse collection of maps. These "diverse map collection" types offer different perspectives, each valuable for specific insights. For instance, a "political map of Iran" provides a clear delineation of international borders, national and provincial capitals, and major cities, offering a macro view of the country's administrative divisions. A "topographic map shows Iran and surrounding countries with international borders," emphasizing the physical features like mountains, rivers, and elevation changes, which are crucial for understanding geographical challenges and opportunities.
Beyond these standard types, specialized maps offer deeper insights. Maps showing "Iran’s nuclear program" and "Israeli airstrikes" provide critical geopolitical context, detailing sensitive sites and areas of conflict. "Iran map city vector divided by outline simplicity style" maps, available in "black thin line version and color of country flag version," offer stylized representations of urban areas and their surrounding regions. These various maps collectively "offer a detailed view of the country’s major regions, key infrastructure, and historical landmarks, making it a valuable resource for anyone interested in Iran." Whether for academic research, strategic analysis, or general interest, the comprehensive collection of Iran border map variations provides an invaluable tool for understanding this complex and fascinating nation.
The Future of Iran's Borders: Challenges and Developments
The future of Iran's borders will undoubtedly be shaped by a confluence of internal developments and external pressures. The challenges of managing a 3,662-mile land border, coupled with critical maritime frontiers, are immense. Issues such as illegal trade, drug smuggling, and the movement of displaced populations will continue to demand significant resources and strategic foresight. The ongoing projects involving "large earth and stone embankments and deep ditches" underscore a commitment to enhancing border security and control, reflecting a proactive approach to these persistent issues.
Furthermore, the geopolitical landscape surrounding Iran remains highly dynamic. Relations with neighboring countries, the evolving situation in Afghanistan and Iraq, and the broader regional power struggles will continue to influence the stability and permeability of Iran's frontiers. The strategic importance of its location, particularly its access to the Persian Gulf and the Caspian Sea, ensures that Iran's borders will remain a focal point of international attention. As global energy demands shift and regional alliances evolve, the Iran border map will continue to be a crucial tool for understanding the country's strategic posture and its role in shaping the future of Western Asia. Continuous monitoring and adaptation of border policies will be essential for Iran to navigate these complexities and secure its vast and vital perimeter.
In conclusion, the Iran border map is far more than a geographical outline; it is a complex tapestry woven from history, politics, geography, and strategic imperatives. From its extensive land boundaries shared with seven nations to its critical maritime access points in the Persian Gulf and Caspian Sea, Iran's borders define its identity and its interactions with the world. Understanding these frontiers is key to appreciating Iran's unique position in Western Asia and the multifaceted challenges and opportunities that lie ahead. We hope this comprehensive guide has provided valuable insights into the intricate world of Iran's borders. What aspects of Iran's geography or geopolitics do you find most intriguing? Share your thoughts in the comments below, or explore our other articles for more detailed analyses of regional dynamics.
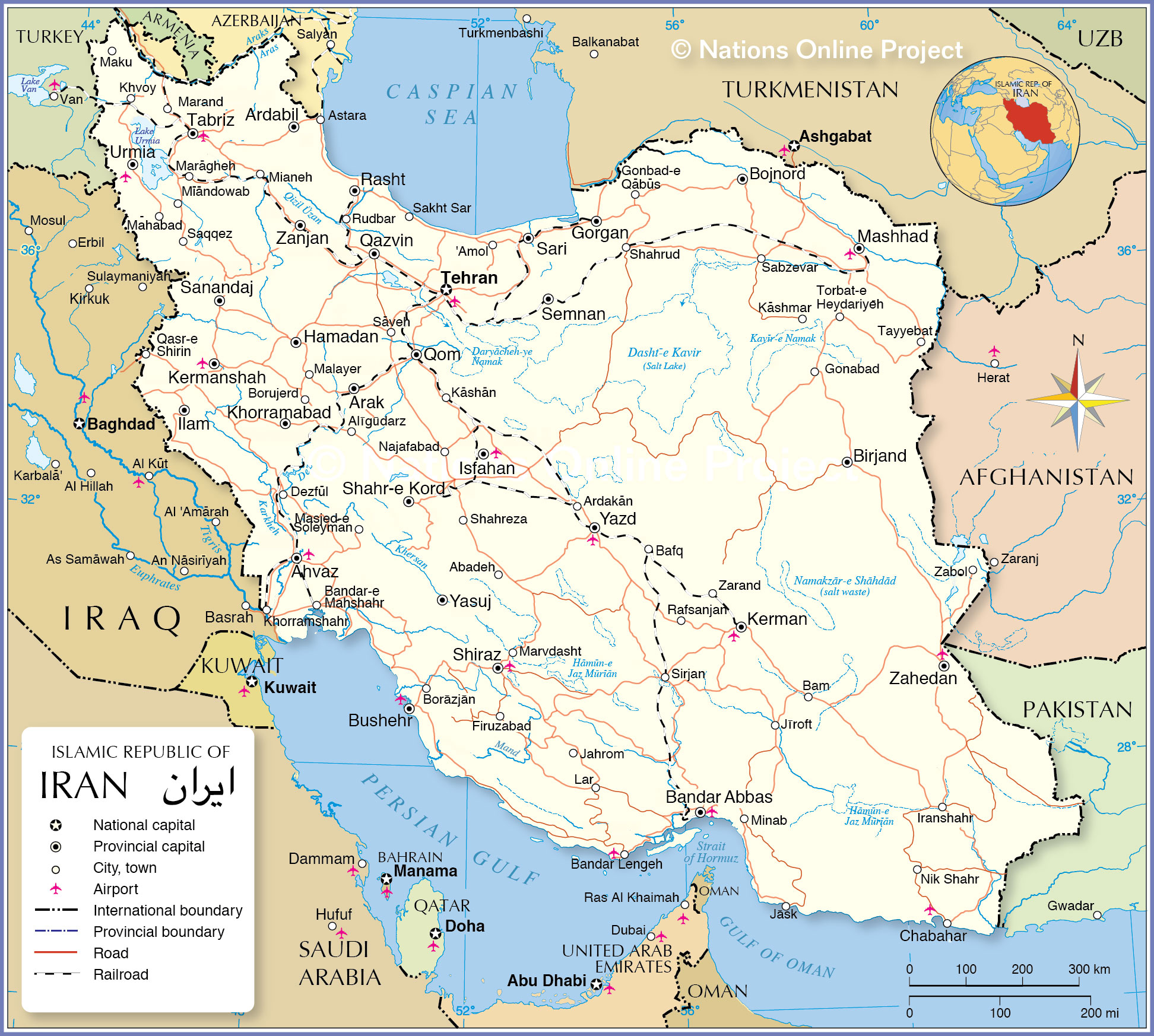
Political Map of Iran - Nations Online Project
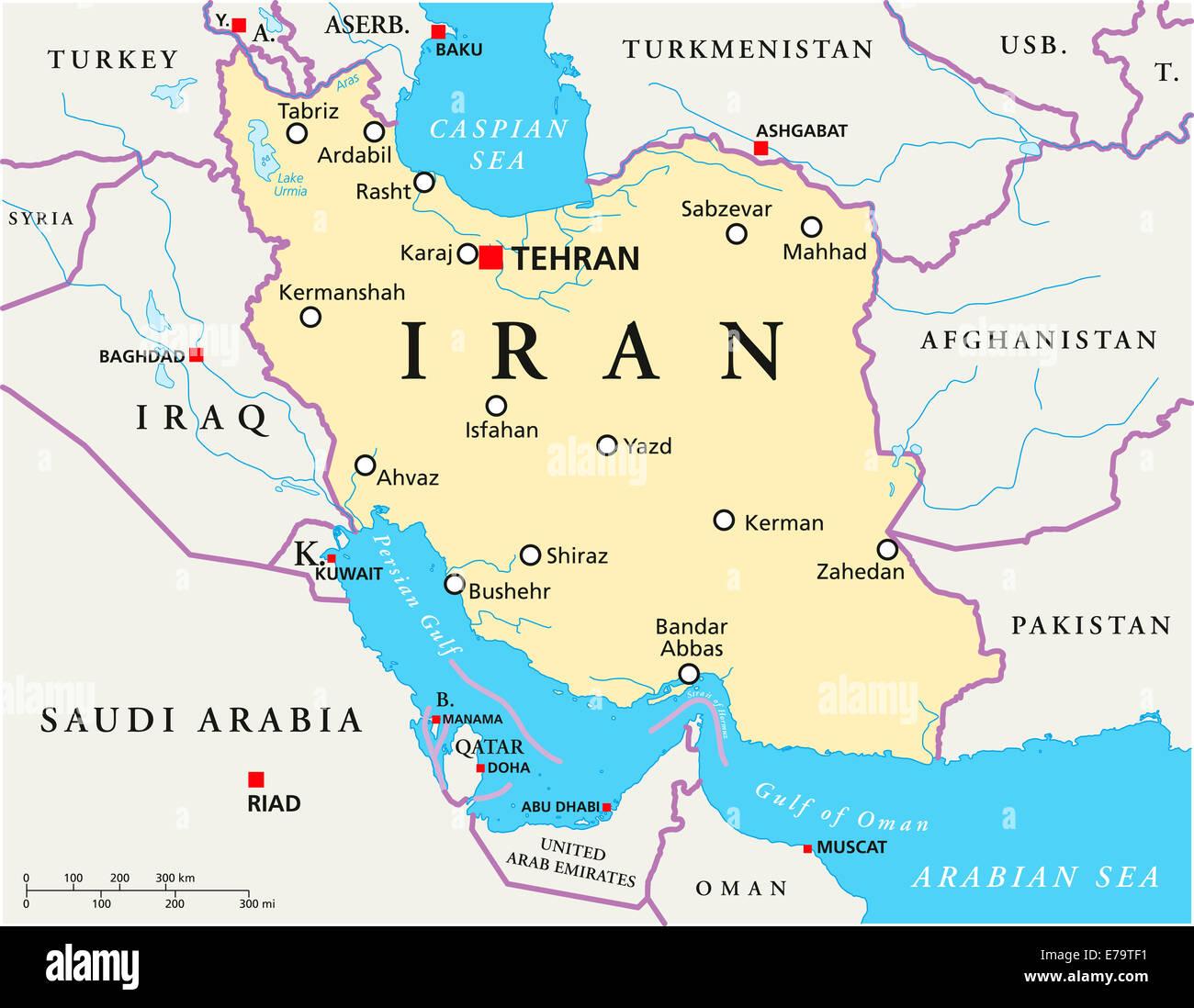
Iran Political Map with capital Tehran, national borders, most
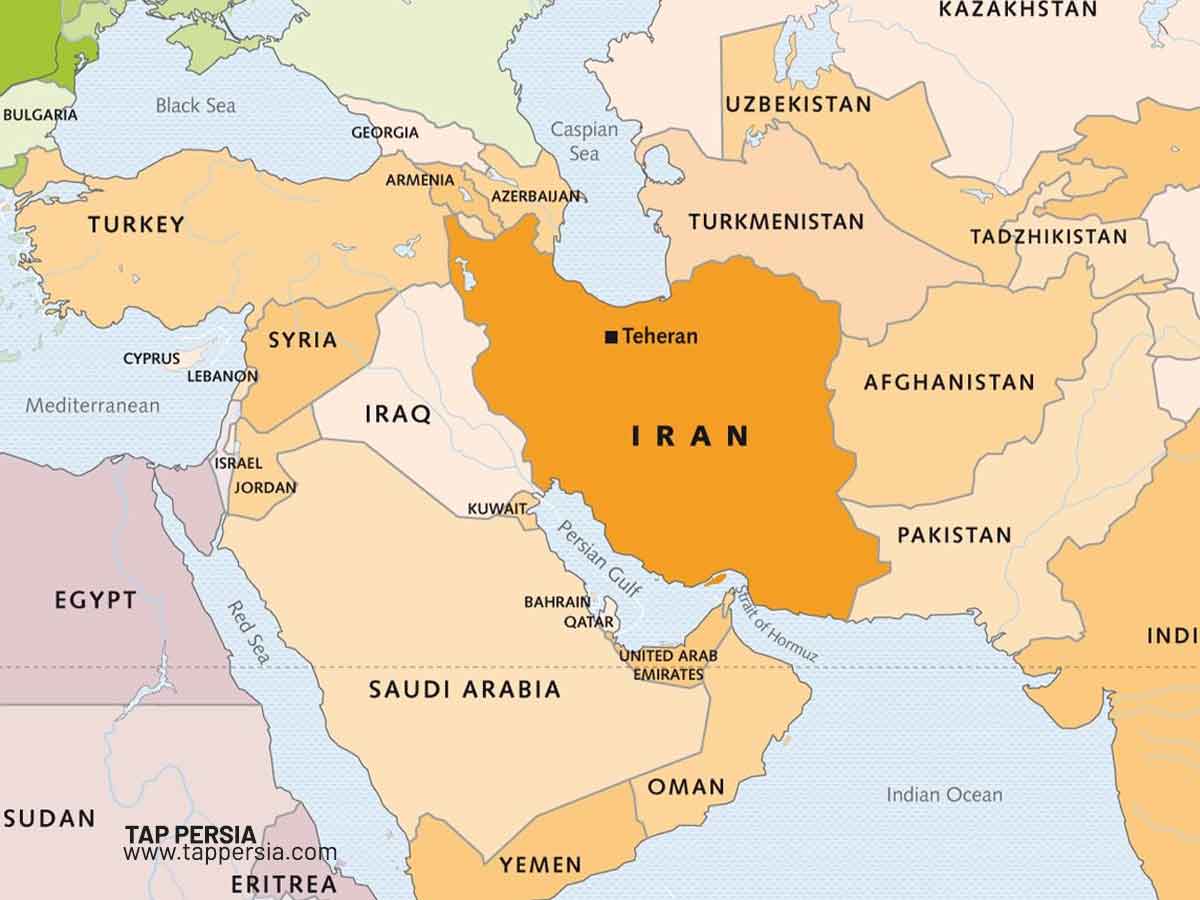
A Comprehensive Guide To Iran Border Crossings |TAP Persia