Unpacking Iran's Capabilities: A Deep Dive Into Regional Power
Iran capabilities represent a multifaceted and evolving strategic landscape, profoundly influencing the geopolitical dynamics of the Middle East. As a pivotal player in the region, Iran's approach to military power reflects both its conventional forces and innovative tactics in asymmetric engagements. Understanding Iran’s military capabilities is essential for appreciating its regional influence and defense posture, especially in light of shifting international relations and ongoing regional tensions.
The incoming American administration is a major development for the region and will likely strengthen Israel while potentially increasing pressure on Iran. This dynamic underscores the critical need to comprehensively assess Iran's strategic assets, from its indigenous nuclear ambitions to its vast missile arsenal and intricate network of proxies. The Defense Intelligence Agency (DIA) today released “Iran Military Power,” an intelligence product that examines the core capabilities of Iran's military, providing crucial details on Iran's defense and military goals, strategy, plans, and intentions. This article delves into these various facets, offering a detailed look at the nation's military and strategic prowess.
Table of Contents
- The Strategic Landscape: Iran's Geopolitical Position
- Iran's Nuclear Ambitions: An Indigenous Pursuit
- A Formidable Conventional Military: Size and Structure
- Iran's Missile Prowess: A Strategic Challenge
- Asymmetric Warfare Strategies: Adapting to Challenges
- External Partnerships: The Russian Connection
- Understanding Iran's Military Evolution and Future Outlook
- Key Takeaways on Iran's Defense Posture
The Strategic Landscape: Iran's Geopolitical Position
Iran's strategic position in the Middle East is undeniably central to regional stability and global energy security. The nation navigates a complex web of alliances, rivalries, and internal pressures that continuously shape its military and foreign policy. The recent shift in the American administration, for instance, is perceived as a major development for the region, expected to strengthen Israel while potentially increasing pressure on Iran. This dynamic directly impacts how Iran perceives its security needs and how it projects its power. For its part, Iran still maintains a focus on an indigenous nuclear capability, viewing it as a cornerstone of its national security. The country's strategic planning is deeply rooted in its historical experiences, including the 1979 Islamic Revolution, which fundamentally reshaped its defense doctrine, leading to a strong emphasis on self-reliance and deterrence. The geopolitical landscape demands a robust assessment of Iran capabilities, not just in terms of raw military might, but also its strategic adaptability and long-term objectives.
Iran's Nuclear Ambitions: An Indigenous Pursuit
Central to discussions about Iran capabilities is its indigenous nuclear program. Despite international scrutiny and sanctions, Iran has consistently pursued the development of nuclear technology, asserting its right to peaceful nuclear energy. However, concerns persist among global powers and regional adversaries that this program could eventually lead to the development of nuclear weapons. Intelligence estimates suggest that while Iran has made significant advancements in enriching uranium, it would need even more time to develop a missile or other means of weaponizing them. This gap between fissile material production and weaponization is a critical factor in the ongoing diplomatic efforts and strategic calculations. The focus on an "indigenous nuclear capability" highlights Iran's determination to achieve self-sufficiency in this sensitive area, driven by perceived security threats and a desire to enhance its deterrent posture. The existence of this program remains a significant strategic challenge in the region, influencing the actions and concerns of countries like Israel and the United States.
A Formidable Conventional Military: Size and Structure
The Iranian armed forces, officially known as the Islamic Republic of Iran Armed Forces, are a formidable entity in the Middle East. Comprising the Islamic Republic of Iran Army (Artesh), the Islamic Revolutionary Guard Corps (Sepah), and the Police Command (Faraja), they are the largest in the Middle East in terms of active troops. This substantial manpower provides Iran with a significant conventional defense capability. However, the structure and deployment of these forces are uniquely tailored to Iran's strategic doctrine, which blends traditional military operations with asymmetric warfare tactics. Understanding the intricate relationship between these branches is crucial for assessing the overall Iran capabilities. While the Artesh largely functions as a conventional military, the IRGC plays a more expansive role, extending its influence beyond national borders through its affiliates and proxies, making it a key instrument of foreign policy and regional power projection.
The Role of the IRGC and Proxies
The Islamic Revolutionary Guard Corps (IRGC) stands as a powerful and influential pillar of Iran's military and political establishment. Unlike a traditional army, the IRGC and its affiliates are not only defensive assets but instruments of foreign policy, extending Iran's reach and influence across the region. This includes supporting various proxy groups, such as Hezbollah in Lebanon, Houthi rebels in Yemen, and various Shiite militias in Iraq and Syria. These proxies serve as an extension of Iran's strategic depth, allowing it to exert pressure, deter adversaries, and respond to threats without direct military confrontation. This network of non-state actors is a critical component of Iran capabilities, enabling asymmetric engagements that can bypass conventional military strength and create complex challenges for its opponents. The IRGC's deep involvement in these networks underscores Iran's strategic approach to regional security and its capacity to project power beyond its borders.
- Faye Maltese
- Chanel West Coast Husband
- Karen Fukuhara Dating
- Who Is Sanaa Lathan Married To
- Nia Peeples Husband
Conventional Forces: Degradation and Resilience
Despite their considerable size, Iran's conventional forces have faced significant challenges. Military operations over the past year, particularly those conducted by Israeli and U.S. forces, are believed to have heavily degraded some of Iran’s conventional assets. This degradation highlights the vulnerability of traditional military infrastructure to sustained air strikes and targeted operations. However, Iran has consistently demonstrated a remarkable capacity for resilience and adaptation. Prior to the 1979 Islamic Revolution, Iran's military was heavily reliant on Western equipment. Following the revolution and subsequent sanctions, Iran embarked on an ambitious program of indigenous military production, complemented by more recent Russian additions. This emphasis on self-sufficiency means that while certain conventional assets may be degraded, Iran's ability to repair, replace, or develop new equipment, often through reverse engineering or domestic innovation, remains a core aspect of its enduring Iran capabilities. This resilience is a testament to its long-term defense strategy.
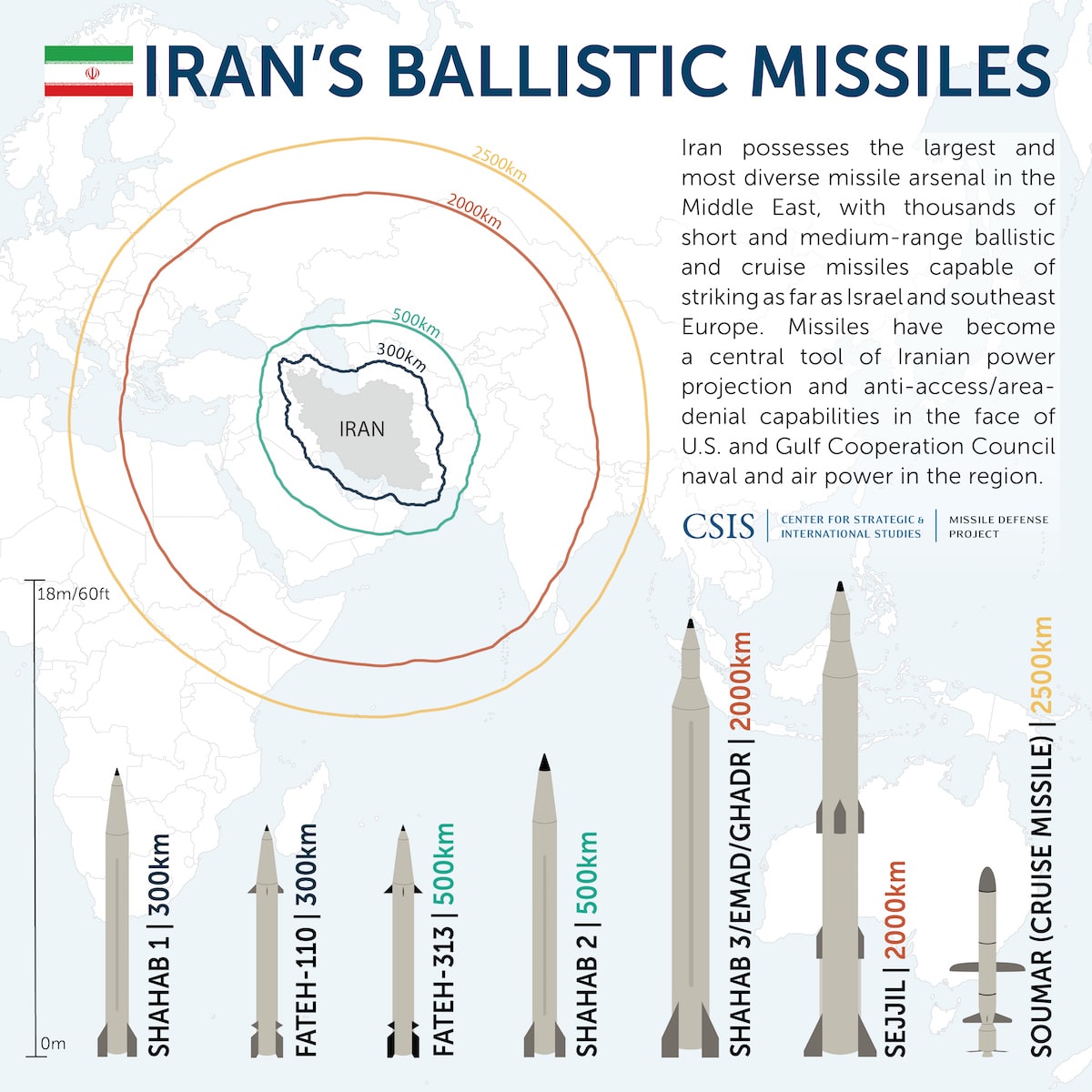
Iran's Missile Prowess: A Strategic Challenge
In addition to its nuclear program, Iran’s missile arsenal presents a significant strategic challenge in the region. The country possesses the region’s largest inventory of ballistic missiles, according to US intelligence, with some reports suggesting Tehran had over 3,000 such missiles before Operation Rising Lion commenced. Intelligence evaluations show Iran maintained approximately 3,000 missiles of various configurations prior to recent conflicts. Iran says its ballistic missiles are an important deterrent and retaliatory force against the U.S., Israel, and other potential regional targets. This vast and diverse arsenal is a cornerstone of Iran capabilities, designed to compensate for perceived weaknesses in conventional air power and to provide a credible threat against distant adversaries. The development of these missiles has been a national priority, with continuous investment in research, development, and production to enhance their range, accuracy, and destructive potential. The sheer scale of this arsenal makes it a primary concern for regional stability and international security.
Ballistic Missile Arsenal: Scope and Range
Iran's ballistic missile arsenal is extensive and varied, showcasing a range of capabilities designed for different strategic purposes. Intelligence estimates suggest Iran has 2,000 ballistic missiles with warheads that can carry 2,000 pounds of explosives or more. These range from shorter-range tactical missiles to longer-range strategic systems. For instance, the Tondar 69, which has a range of 150km (93 miles), is designed for closer targets, while more advanced missiles like the Khorramshahr are capable of reaching much greater distances, potentially threatening targets across the Middle East and beyond. The continuous development and deployment of these missiles, often showcased in military parades and exercises, underscore Iran's commitment to enhancing its deterrent capabilities. Witkoff also raised concerns about Iran's ballistic missile arsenal during a speech in New York on Wednesday, calling it as big of an existential threat for Israel as Iran's nuclear capabilities. This highlights the severe regional apprehension regarding the scope and reach of Iran's missile program.
Cruise Missiles and Air Power
Beyond ballistic missiles, Iran has varied air power capabilities, including deep and diverse arsenals of cruise and other advanced air-launched weapons. As demonstrated in its air strikes against Israel in 2024, Iran has utilized these capabilities to project power and retaliate against perceived threats. The effectiveness of these strikes, even if partially intercepted, showcased Iran's ability to coordinate complex missile and drone attacks. Iran has also used these missiles to hit militants, demonstrating their utility in counter-terrorism operations and regional engagements. The integration of cruise missiles, which can fly at lower altitudes and evade radar more effectively than ballistic missiles, adds another layer of complexity to Iran's offensive capabilities. This blend of ballistic and cruise missiles, coupled with its growing drone fleet, provides Iran with a versatile array of options for both deterrence and offensive action, significantly enhancing its overall Iran capabilities in the air domain.
Asymmetric Warfare Strategies: Adapting to Challenges
Iran’s military capabilities and asymmetric warfare strategies have garnered significant attention in recent years. Recognizing that it cannot match the conventional military might of some of its adversaries, Iran has strategically invested in asymmetric tactics to level the playing field. This involves leveraging its unique geographical features, developing low-cost, high-impact weapons systems like drones and anti-ship missiles, and cultivating a robust network of proxy forces. These innovative tactics in asymmetric engagements allow Iran to inflict disproportionate costs on its opponents, complicate their strategic planning, and project influence without direct, large-scale military confrontation. From naval harassment in the Strait of Hormuz to cyber warfare and support for insurgent groups, Iran's asymmetric approach is designed to create dilemmas for its adversaries and to protect its national interests through unconventional means. This adaptive strategy is a core component of its overall Iran capabilities, making it a challenging and unpredictable actor in regional conflicts.
External Partnerships: The Russian Connection
Iran's strategic partnerships play a crucial role in enhancing its military capabilities and technological advancement. Its partnership with defense power Russia has also been beneficial, providing Iran with access to advanced military hardware and technical expertise that might otherwise be unavailable due due to international sanctions. This collaboration is not a recent phenomenon; elements of Iran's military inventory, particularly its air defense systems and some armored vehicles, show influences from Russian designs that predate the 1979 Islamic Revolution, along with more recent Russian additions. The ongoing war in Ukraine has further deepened this relationship, with reports suggesting Iran has supplied Russia with drones, and in return, potentially received advanced military technology. These partnerships help Iran circumvent sanctions, modernize its forces, and acquire sophisticated systems that bolster its defense and offensive Iran capabilities. This strategic alignment with major global powers like Russia allows Iran to diversify its military procurement and enhance its geopolitical leverage.
Understanding Iran's Military Evolution and Future Outlook
Iran’s military capabilities have evolved significantly over the years, presenting a complex landscape of strategic assets and doctrines. From a military largely reliant on Western equipment before the 1979 revolution, Iran has transformed into a nation emphasizing indigenous production and asymmetric warfare. This volume in DIA's series of military power reports provides details on Iran's defense and military goals, strategy, plans, and intentions, offering valuable insights into its future trajectory. Understanding Iran’s military capabilities compared to its regional counterparts and global powers is essential for appreciating its regional influence and defense posture. The nation continuously adapts its strategies in response to perceived threats and geopolitical shifts, investing in areas where it can achieve maximum impact, such as its missile program and proxy networks. The future outlook for Iran's military involves continued efforts to enhance its self-sufficiency, modernize its forces, and refine its asymmetric warfare tactics, ensuring it remains a formidable and influential player in the Middle East.
Key Takeaways on Iran's Defense Posture
In summary, Iran capabilities are a complex blend of conventional military strength, advanced missile technology, an indigenous nuclear program, and sophisticated asymmetric warfare strategies. While its conventional forces have faced degradation, their sheer size and Iran's commitment to self-sufficiency ensure resilience. The nation's vast missile arsenal, particularly its ballistic and cruise missiles, serves as a powerful deterrent and a significant strategic challenge to regional and global security. The pivotal role of the IRGC and its network of proxies extends Iran's influence far beyond its borders, enabling a unique form of power projection. Furthermore, strategic partnerships, notably with Russia, contribute to the modernization and technological advancement of its military. As Iran continues to navigate a volatile geopolitical landscape, its evolving defense posture and multifaceted Iran capabilities will remain a critical factor in shaping the future of the Middle East.
We hope this comprehensive overview has provided valuable insights into Iran's military and strategic prowess. What are your thoughts on Iran's evolving capabilities and their impact on regional stability? Share your perspectives in the comments below, or explore our partner site Warpower to view the inventory breakdown of Iran and other nations. Your engagement helps foster a deeper understanding of these critical geopolitical dynamics.
- Chanel Santini Age
- Logan Paul Dating History
- Who Is Whitney Cummings Dating
- Terri Welles Playmate
- Mario Casas Sierra

Iran TV: Iran will strengthen its missile capabilities

Iranian military capabilities have evolved despite arms embargo – IFMAT
Missiles of Iran | Missile Threat